How To Create Log File In Java Using Log4j Example
Log4j hello world example
In this tutorial, we will show you how to use the classic log4j 1.2.x to log a debug or error message in a Java application.
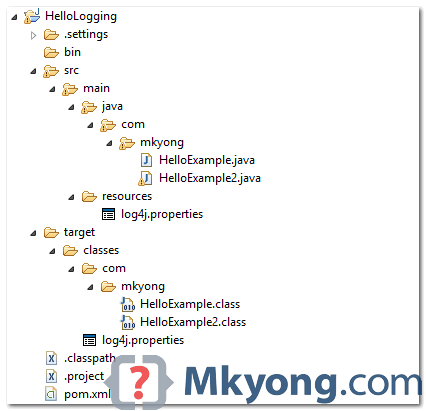
1. Project Directory
Review the final project structure, a standard Maven style Java project.
2. Get Log4j
Declares the following dependencies :
pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> For non-Maven user, visit log4j official page, download the jar and put it in the project library path manually.
3. log4j.properties
Create a log4j.properties file and put it into the resources folder. Refer to the step #1 above.
Note
- For standalone Java app, make sure the
log4j.propertiesfile is under theproject/classesdirectory - For Java web applications, make sure the
log4j.propertiesfile is under theWEB-INF/classesdirectory
log4j.properties
# Root logger option log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout, file # Redirect log messages to console log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n # Redirect log messages to a log file, support file rolling. log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender log4j.appender.file.File=C:\\log4j-application.log log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=5MB log4j.appender.file.MaxBackupIndex=10 log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n Note
To understand the symbols in the ConversionPattern, please refer to this log4j PatternLayout guide.
Let break it down :
- %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} = Date and time format, refer to SimpleDateFormat JavaDoc.
- %-5p = The logging priority, like DEBUG or ERROR. The -5 is optional, for the pretty print format.
- %c{1} = The logging name we set via getLogger(), refer to log4j PatternLayout guide.
- %L = The line number from where the logging request.
- %m%n = The message to log and line break.
Log message examples :
2014-07-02 20:52:39 DEBUG className:200 - This is debug message 2014-07-02 20:52:39 DEBUG className:201 - This is debug message2 4. Demo – How to log a Message?
To log a message, first, create a final static logger and define a name for the logger, normally, we use the full package class name.
final static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(classname.class); Then, logs messages with different priorities, for example, debug, info, warn, error and fatal. Normally, you just need to use debug or error.
//logs a debug message if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){ logger.debug("This is debug"); } //logs an error message with parameter logger.error("This is error : " + parameter); //logs an exception thrown from somewhere logger.error("This is error", exception); 4.1 Example : Logger is set to debug priority.
log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout #... HelloExample.java
package com.mkyong; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; public class HelloExample{ final static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(HelloExample.class); public static void main(String[] args) { HelloExample obj = new HelloExample(); obj.runMe("mkyong"); } private void runMe(String parameter){ if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){ logger.debug("This is debug : " + parameter); } if(logger.isInfoEnabled()){ logger.info("This is info : " + parameter); } logger.warn("This is warn : " + parameter); logger.error("This is error : " + parameter); logger.fatal("This is fatal : " + parameter); } } Output
2014-07-02 20:52:39 DEBUG HelloExample:19 - This is debug : mkyong 2014-07-02 20:52:39 INFO HelloExample:23 - This is info : mkyong 2014-07-02 20:52:39 WARN HelloExample:26 - This is warn : mkyong 2014-07-02 20:52:39 ERROR HelloExample:27 - This is error : mkyong 2014-07-02 20:52:39 FATAL HelloExample:28 - This is fatal : mkyong 4.2 Example – Logger is set to error priority.
log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=error, stdout #... Run the HelloExample again, you will get the following output
2014-07-02 20:56:02 ERROR HelloExample:27 - This is error : mkyong 2014-07-02 20:56:02 FATAL HelloExample:28 - This is fatal : mkyong Review the log4j's Priority class.
Priority.java
package org.apache.log4j; public class Priority { public final static int OFF_INT = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public final static int FATAL_INT = 50000; public final static int ERROR_INT = 40000; public final static int WARN_INT = 30000; public final static int INFO_INT = 20000; public final static int DEBUG_INT = 10000; //public final static int FINE_INT = DEBUG_INT; public final static int ALL_INT = Integer.MIN_VALUE; If priority is defined in log4j.properties, only the same or above priority message will be logged.
5. Demo – How to log an Exception
An example to show you how to use log4j to log an exception.
HelloExample2.java
package com.mkyong; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; public class HelloExample2{ final static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(HelloExample2.class); public static void main(String[] args) { HelloExample2 obj = new HelloExample2(); try{ obj.divide(); }catch(ArithmeticException ex){ logger.error("Sorry, something wrong!", ex); } } private void divide(){ int i = 10 /0; } } Output
2014-07-02 21:03:10 ERROR HelloExample2:16 - Sorry, something wrong! java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.mkyong.HelloExample2.divide(HelloExample2.java:24) at com.mkyong.HelloExample2.main(HelloExample2.java:14) Done.
Download Source Code
References
- log4j 1.2 official page
- log4j pattern layout
- Wikipedia : log4j
- Spring MVC + log4j example
- log4j.properties examples
Comments
How To Create Log File In Java Using Log4j Example
Source: https://mkyong.com/logging/log4j-hello-world-example/
Posted by: bentleyswuzzin.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Log File In Java Using Log4j Example"
Post a Comment